Uncategorized
The Benefits of Taurine for Endurance Athletes
Many athletes are reaping the benefits of taurine for endurance. If you are curious about how taurine can improve your endurance, keep reading.
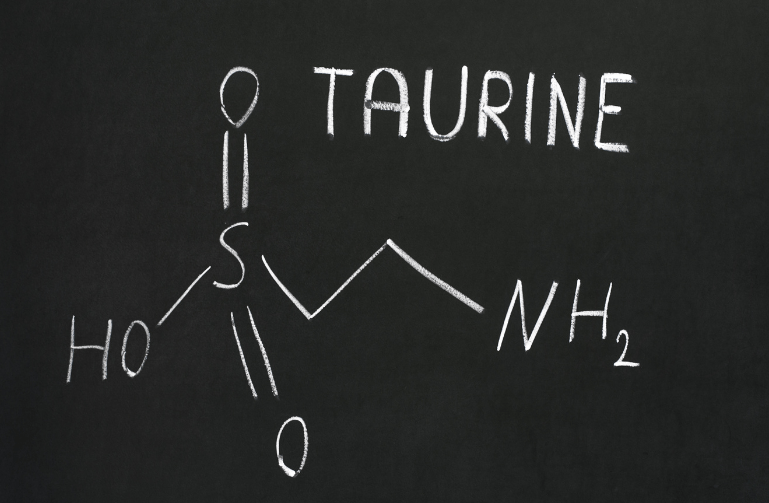
What is Taurine?
Let’s change things up a bit from my normal routine and start with a fun fact about taurine. I feel like it has been a while since I had a quality fun fact to share, and this one is a doozie. Taurine is derived from the Latin term taurus, which translates to bull or ox. But that’s not the fun part. This is: taurine was originally isolated from bull semen and ox bile. Super fun! You might have even heard rumors that a certain energy drink (we won’t mention any names) contains taurine derived from bull semen. I checked their website, and fortunately, their energy drink contains synthetically made taurine. Luckily for everyone, including the animals, taurine is now synthetically produced for supplementation as well. Okay, back to the topic at hand.
Taurine is considered a conditional amino acid because it is derived from cysteine, like other amino acids, but taurine lacks a carboxyl group that amino acids typically have. Quite simply, taurine plays a large role in energy metabolism. Energy metabolism is a simple process by which the body acquires and utilizes energy to maintain normal function (Wen et al., 2018). Furthermore, taurine plays an important role in skeletal muscle function (Seidel et al., 2019). Foods such as turkey, seafood, and seaweed contain the most amounts of taurine. It is also taken as a dietary and fitness supplement, especially by endurance athletes. You will also find taurine on the ingredient list of many energy drinks.
taurine plays a large role in energy metabolism. Energy metabolism is a simple process by which the body acquires and utilizes energy to maintain normal function (Wen et al., 2018). Furthermore, taurine plays an important role in skeletal muscle function (Seidel et al., 2019). Foods such as turkey, seafood, and seaweed contain the most amounts of taurine. It is also taken as a dietary and fitness supplement, especially by endurance athletes. You will also find taurine on the ingredient list of many energy drinks.
What are the Benefits of Taurine for Endurance Athletes?
Here is a short explanation of the benefits of taurine for endurance athletes:
- Prevents taurine deficiency- which I probably did not need to tell you.
- Increases fat oxidation (Imagawa et al., 2009)
- Improves endurance performance (Imagawa et al., 2009)
- Decreases muscle soreness (Ra et al., 2013)
- Improves time to exhaustion (Yatabe et al., 2009)
- Decreases muscle damage (Ra et al., 2013)
For all my science-loving friends:
Da Silva et al. (2014) studied the effects of taurine supplementation on muscle performance and oxidative stress. During their study, performance was measured on days 1, 14, 16, 18, and 21 after starting the taurine or placebo supplement. The results showed that taurine supplementation resulted in increased muscle strength levels and decreased muscle soreness. These results suggest that taurine supplementation can improve performance and decrease muscle damage. Seidel et al. (2019) found similar results in that their study showed reduced muscle damage when taurine was supplemented.
Another study observed the relationship between taurine supplementation and oxidative stress. If you do not know, oxidative stress is simply an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. Concerning endurance sport, oxidative stress can result from overused muscles. Thirupathi et al. (2020) found that short-term supplementation with taurine increased performance during intense exercise and reduced oxidative damage in muscles.
The scientific literature also supports that taurine supplementation improves endurance performance. Yatabe et al. (2009) found that oral taurine supplementation reduced exercise-induced muscle fatigue and increased total time to exhaustion. Imagawa et al. (2009) found that endurance performance and fat oxidation both increased after a two-week period of taurine supplementation. Additionally, taurine significantly decreased lactate accumulation after running long distances (sound familiar ultra-runners?) (Ra et al., 2013).

Kurtz et al. (2021) published a literature review of the current research findings on taurine supplementation in sports and exercise. Here is a brief list of their findings:
- Improved VO2 max
- Increased time to exhaustion
- Increased anaerobic performance
- Reduced muscle damage
- Improved recovery
- Reduced inflammatory markers
Isn’t this sounding more and more like the perfect supplement for endurance athletes to add to their regimen?
How Should I Take Taurine for Endurance?
Now that I have convinced you that taurine is an excellent supplement for endurance athletes let’s talk about the best ways to take a taurine supplement.
Taurine is most effective as a supplement when taken every day. This is especially true for those who regularly supplement beta-alanine, which can actually cause a taurine deficiency. Those who follow a plant-based diet can also suffer from taurine deficiency because very few plant-based foods contain taurine. The research shows that the scientifically effective dose of taurine is between 500 mg and 6 grams (Waldron et al., 2018). I know that sounds like a pretty wide range, and I don’t disagree with that, but I can’t argue with the science. Additionally, the tolerable upper intake level is pretty forgiving. Taking 3 grams of taurine daily over a lifetime should produce no adverse effects (Shao & Hathcock, 2008).
Where Can I Find a Taurine Supplement?
Now, let’s wrap this up with a neat little bow. I know for a fact that I have convinced you that taurine is a legitimate supplement with amazing benefits for endurance athletes. Who wouldn’t want to have improved performance, decreased muscle soreness, increased time to exhaustion, and decreased muscle damage? If you don’t want those things, then I guess you mistakenly read through this entire blog. But if you do want those benefits, you are probably wondering what you should take. If so, you are in luck. Here at Ultraverse Supplements, we have included 1.5 grams of taurine in our daily endurance supplement, T – 30. And because we are nice people, we used the synthetic version rather than the stuff made from bull semen or ox bile…you’re welcome!
 If you want to learn more about this premium endurance supplement, please read Chase’s blog. It has some great information on the amazing ingredients in T – 30, and if this blog wasn’t enough to convince you to take it, his blog will…hopefully.
If you want to learn more about this premium endurance supplement, please read Chase’s blog. It has some great information on the amazing ingredients in T – 30, and if this blog wasn’t enough to convince you to take it, his blog will…hopefully.
**Use common sense, and always listen to your doctor over a blog post. They know more about your personal health situation than anybody behind a keyboard. If you have underlying medical conditions, always check with your doctor before starting a new supplementation routine.
References
da Silva, L. A., Tromm, C. B., Bom, K. F., Mariano, I., Pozzi, B., da Rosa, G. L., . . . Pinho, R. A. (2014). Effects of taurine supplementation following eccentric exercise in young adults. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism = Physiologie Appliquee, Nutrition Et Metabolisme, 39(1), 101-104. doi:10.1139/apnm-2012-0229 [doi]
magawa, T. F., Hirano, I., Utsuki, K., Horie, M., Naka, A., Matsumoto, K., & Imagawa, S. (2009). Caffeine and taurine enhance endurance performance. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 30(7), 485–488. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1104574
Kurtz, J. A., VanDusseldorp, T. A., Doyle, J. A., & Otis, J. S. (2021). Taurine in sports and exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 18(1), 39-0. doi:10.1186/s12970-021-00438-0
Ra, S.-G., Miyazaki, T., Ishikura, K., Nagayama, H., Komine, S., Nakata, Y., Maeda, S., Matsuzaki, Y., & Ohmori, H. (2013). Combined effect of branched-chain amino acids and taurine supplementation on delayed onset muscle soreness and muscle damage in high-intensity eccentric exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 10(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.1186/1550-2783-10-51
Seidel, U., Huebbe, P., & Rimbach, G. (2019). Taurine: A regulator of cellular redox homeostasis and skeletal muscle function. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 63(16), 1800569.
Thirupathi, A., Pinho, R. A., Baker, J. S., István, B., & Gu, Y. (2020). Taurine reverses oxidative damages and restores the muscle function in overuse of exercised muscle. Frontiers in Physiology, 11, 582449. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.582449
Waldron, M., Patterson, S. D., Tallent, J., & Jeffries, O. (2018). The Effects of an Oral Taurine Dose and Supplementation Period on Endurance Exercise Performance in Humans: A Meta-Analysis. Sports Medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), 48(5), 1247–1253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-018-0896-2
Wen, C., Li, F., Zhang, L., Duan, Y., Guo, Q., Wang, W., . . . Yin, Y. (2019). Taurine is involved in energy metabolism in muscles, adipose tissue, and the liver. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 63(2), 1800536.
Yatabe, Y., Miyakawa, S., Ohmori, H., Mishima, H., & Adachi, T. (2009). Effects of taurine administration on exercise. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 643, 245–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-75681-3_25